Updated: May 10, 2024
Published: January 19, 2023
Even though ERP and CRM applications are very distinctive and cover different areas of business processes, sometimes, it makes sense to compare ERP vs CRM and see which solution will be better. In this article, we will explain both Enterprise Resource Planning and Customer Relationship Management software and provide an overview of use cases to help you with the choice.
List of the Content
- Introduction to ERP and CRM systems
- Key differences between ERP and CRM
- Use cases for ERP and CRM
- Key features of ERP and CRM systems
- Choosing between ERP and CRM
- ERP vs CRM: implementation and maintenance cost
- Conclusion
INTRODUCTION TO ERP AND CRM SYSTEMS
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems are two software types commonly used in businesses to manage various aspects of operations and customer interactions. While they are often used in conjunction with each other, these systems serve different purposes and are used to support different business processes.
ERP systems are designed to support and automate various business processes, including accounting, inventory management, human resources, and supply chain management. They aim to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s resources and activities and help streamline the flow of information between different departments and functions.
On the other hand, CRM systems focus on managing customer interactions and relationships. They are used to track customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle, including marketing, sales, and service. CRM systems help businesses to better understand their customers’ needs and preferences and provide tools for automating and improving customer-facing processes such as sales, marketing, and customer service.
ERP and CRM systems can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud and are typically accessed via a web browser or a mobile app. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization and can be integrated with other software and systems such as email, project management, and data analytics tools.
ERP and CRM systems are used by businesses of all sizes across a wide range of industries. They can be beneficial for organizations that have complex operations, multiple locations, or a large number of customers. However, implementing and maintaining these systems can be costly, and time-consuming, and requires careful planning and ongoing support.
In summary, ERP and CRM systems are powerful tools that can help businesses to improve efficiency, streamline operations, and better serve their customers. While they serve different purposes and are used to support different business processes, they can be used together to create a more cohesive and integrated view of an organization’s resources and activities.
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ERP AND CRM
While they are often used in conjunction with each other, these systems serve different purposes and are used to support different business processes. Here are some key differences between ERP and CRM systems:
- Business processes: ERP systems support various business processes, including financial management, supply chain management, and manufacturing. They aim to provide a single, integrated system for managing an organization’s resources and activities. On the other hand, CRM systems focus specifically on managing customer-facing processes such as sales, marketing, and customer service.
- Data management: ERP systems are designed to manage and integrate data from various business functions and departments, such as accounting, inventory management, and human resources. They provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s resources and activities to streamline the flow of information between different departments and functions. On the other hand, CRM systems focus on managing customer data and interactions. They are used to track customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle, including marketing, sales, and service.
- Scope: ERP systems are typically more complex and cover a wider range of business processes than CRM systems. They provide a broad view of an organization’s resources and activities, and can be customized to meet the business’s specific needs. CRM systems typically cover only data that are related to the records about the customers
- Implementation and maintenance: ERP and CRM systems can be complex and require careful planning and ongoing support to maintain and update. However, ERP systems are more expensive and time-consuming to implement due to their broader scope and the need to integrate data from multiple departments and functions. CRM systems, on the other hand, are typically easier and faster to implement. Most of the time, CRM systems can be used as designed by the vendors and require small to no customization.
- User base: ERP systems are typically used by various employees across different departments and functions. They provide a single, integrated system for managing an organization’s resources and activities. On the other hand, CRM systems are typically used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams and are focused specifically on managing customer interactions and relationships.
USE CASES FOR ERP AND CRM
As mentioned above, when comparing ERP vs CRM, it is essential to remember that those applications are built for different purposes. Thus the use cases are very different. ERPs are primarily used in departments that don’t face the customer, such as manufacturing and accounting. On the contrary, sales and marketing teams leverage CRM solutions as their main software for daily operations. At first glance, the difference might be obscure. For a better explanation, here are some use cases for you to better understand the differences between ERP and CRM.
Sales
The sales teams use CRMs to track customer information, such as contact details and purchase history, and manage interactions, such as sales and support inquiries. One of the primary use cases for CRM systems is in sales and marketing. By using a CRM system, a sales team can access detailed information about their leads and customers, which can help them close deals more effectively. Additionally, a CRM system can be used to automate and manage marketing campaigns, which can help to generate more leads and increase conversion rates.
Manufacturing and supply chain
ERP systems are designed to integrate and automate the various functions of a business, such as accounting, inventory management, human resources, and production. This allows for more efficient and accurate data tracking and improved communication and collaboration between different departments. One of the primary use cases for ERP systems is in manufacturing and supply chain management. For example, an ERP system could be used to track inventory levels, schedule production runs, and manage the logistics of shipping and receiving. This would enable a company to respond more quickly to customer demand and better use its resources.
Service Sector
In the service sector, ERP and CRM can be used in conjunction to improve overall operations. For example, in a service-based company, where customer engagement is key to success, a CRM system can be used to track customer interactions, such as requests for service and support, and efficiently manage them. Additionally, an ERP system can be used to manage the logistics of service delivery, such as scheduling and resource allocation, which can help to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Retail and e-commerce
Another use case for ERP systems is in retail and e-commerce. By integrating their point-of-sale system, inventory management, and accounting functions, a retail business can gain real-time visibility into sales data and inventory levels, which allows them to make better-informed decisions. Additionally, they could use the system to track customer purchase history, which can help with marketing and sales efforts.
Healthcare
The medical industry is an interesting case to discuss. Healthcare leverages numerous electronic records and management software. Typical healthcare ERP is a specialized Hospital management system (HMS) or Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system. These applications contain both data and workflow management components. Since ERP can incorporate a CRM module, it is safe to bring healthcare as an example among industries that use ERPs.
How does the hospital management system work?
Healthcare providers can use an ERP system to manage patient information, schedule appointments, and track billing and insurance claims. This allows for more efficient and accurate data tracking and improved communication and collaboration between different departments. With the integration of an ERP system, healthcare providers can easily access patient information and make informed decisions in real time, which can help to improve patient outcomes.
On the other hand, the CRM component can be particularly useful in the healthcare industry for managing customer engagement and retention. Healthcare providers can use a CRM system to track and manage patient interactions, such as appointments and follow-up visits, and interactions with insurance companies and other stakeholders. This allows for more efficient and effective communication and engagement with patients, which can help to improve patient satisfaction and loyalty.
Construction
ERP and CRM systems can also be used in the construction industry. An ERP system can manage financials, procurement, and project management, while a CRM system can manage customer and vendor interactions. This can improve efficiency and coordination between different departments and improve the overall project management process.
Services and support
Customer facing is the primary example where CRM systems are the kings. A company can track and manage customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback. This allows them to respond more quickly and effectively to customer needs and can also be used to identify and address common problems or areas for improvement. Additionally, a CRM system can also be used to track customer satisfaction and loyalty, which can be used to inform marketing and sales efforts.
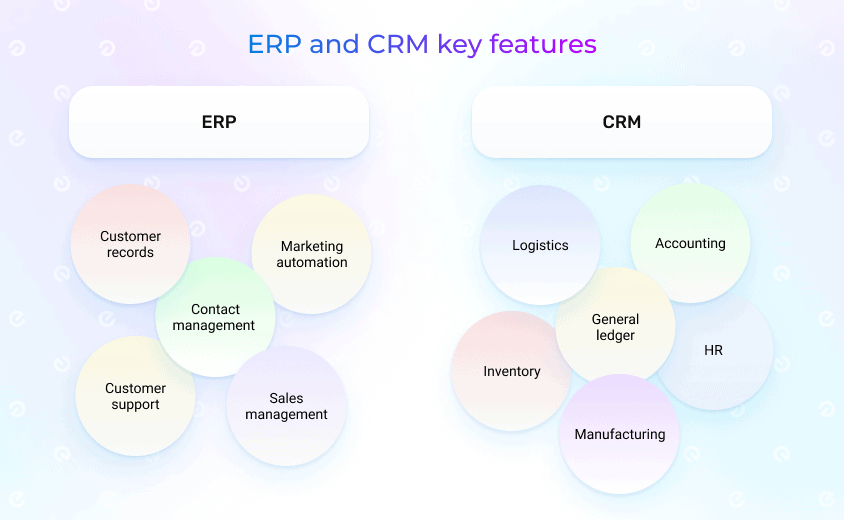
KEY FEATURES OF ERP AND CRM SYSTEMS
When comparing ERP vs CRM, it is important to mention that ERPs can be vast system covering everything that is going on inside the company and business processes. As a result, the list of ERP features will be way bigger compared to the list of CRM features. Nevertheless, both systems have different features and functionalities, but they can also be integrated to create a more comprehensive solution.
First, here are typical features that are included in the ERPs on a regular basis. Of course, depending on the business type and needs, the list can be shorter or way bigger:
- Accounting: One of the most important features of an ERP system is its ability to manage financial transactions, such as invoicing, accounts payable, and general ledger. This allows for more efficient and accurate data tracking and improved communication and collaboration between different departments. The accounting feature of an ERP system allows businesses to keep track of all financial transactions, from invoicing to the general ledger. This can be helpful for businesses of all sizes, especially those with multiple locations, to have a single source of truth for financial data and reporting.
- Inventory Management: An ERP system can be used to track inventory levels, schedule production runs, and manage the logistics of shipping and receiving. This can help businesses respond more quickly to customer demand and better use their resources. Inventory management features on ERP allow businesses to have real-time visibility on stock levels, locations, and orders. Additionally, some ERP systems may also have the functionality to automatically generate purchase orders and track supplier performance, which can help improve the supply chain’s efficiency.
- Human Resources: An ERP system can be used to manage employee information, such as payroll, benefits, and performance evaluations. This allows for more efficient and accurate data tracking and improved communication and collaboration between different departments. HR features can include employee data management, payroll, benefits administration, and scheduling, as well as tracking employee performance and managing training and development.
- Supply Chain Management: An ERP system can be used to manage the logistics of the supply chain, such as tracking inventory levels, scheduling production runs, and managing the logistics of shipping and receiving. This can help businesses improve efficiency and coordination between different departments and improve the overall project management process. The supply chain management feature in ERP can also provide inventory forecasting and demand planning functionalities, which can help improve the supply chain’s efficiency.
- Project Management: Some ERP systems may have a project management feature that allows businesses to manage their projects from end-to-end, from budgeting, resource allocation, task assignment, time tracking, and project performance reporting.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Most ERP systems will include an array of reporting tools, which can be used to generate real-time data and analytics on various aspects of business operations. This can help businesses to make better-informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
Want to know more about ERP applications’ features?
In this article, you’ll find more detailed information on every ERP module and workflow.
When it comes to CRM systems, they are mainly designed to store data about interactions with customers. Modern businesses can have hundreds of records specifically assigned to millions of customers. Sales and customer service teams should be able to access the information about the client quickly and conveniently to make the interactions as smooth as possible. It is important to provide a personal and data-driven attitude for every customer and create segments of the customers based on their behavior and other attributes for the marketing team. Here are the things that CRM systems cover:
- Contact Management: One of the most essential features of a CRM system is its ability to track customer information, such as contact details and purchase history. This allows businesses to have a centralized location for customer data and improve customer communication. The contact management feature in the CRM system allows businesses to store customer data, like contact information, purchase history, and communication logs, in one central location.
- Sales Management: CRM systems can be used to manage sales efforts by providing detailed information about leads and customers and automating and managing marketing campaigns. This can help sales teams to close deals more effectively and increase conversion rates. Sales management features in a CRM system can include lead tracking, sales forecasting, and pipeline management.
- Marketing Automation: CRM systems can be used to automate and manage marketing campaigns, such as email campaigns, segmentation, and personalization. This can generate more leads and increase conversion rates. Marketing Automation in CRM systems can also provide analytics and reporting on the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service and Support: CRM systems can be used to track and manage customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback. This allows businesses to respond more quickly and effectively to customer needs and can also be used to identify and address common problems or areas for improvement. This feature can also be integrated with helpdesk and call center functionalities, enabling customer service agents to access customer data, view history, and take action in real-time.
- Analytics and Reporting: CRM systems can be used to track customer satisfaction and loyalty, which can be used to inform marketing and sales efforts. The reporting feature in CRM systems provides businesses with real-time data and analytics on customer interactions, which can be used to improve customer service and sales efforts.
- Mobile Access: CRM systems are often accessible via mobile apps and web browsers, which allows businesses to access customer information and take action from anywhere. This can improve communication and engagement with customers and improve the efficiency of sales and customer service efforts on-site.
- Integration: Many CRM systems can be integrated with other business systems, such as accounting and inventory management systems, social media platforms, or ERPs. This can provide a more comprehensive view of customer interactions and allow businesses to make better-informed decisions.
- Personalization: Some CRM systems can be used to create highly personalized and targeted marketing campaigns based on customer data and behavior. This can help to increase conversion rates and improve customer satisfaction.
- Predictive Analytics: Some CRM systems can also be used to analyze customer data and behavior to predict future trends and behavior. This can be used to inform marketing and sales efforts, as well as identify potential issues and opportunities.
- Collaboration: Collaboration features can be found in some CRM systems, which allow teams to share and access customer data, collaborate on tasks and projects, and receive real-time updates. This can improve communication and collaboration between different departments and teams.
- Automation: Many CRM systems include automation features that can help to improve the efficiency of sales and customer service efforts. These features can include automated email campaigns, appointment scheduling, and automated task assignments.
When you compare ERP vs CRM, it might look like CRMs are much smaller. But those applications are as important as Enterprise Resource Planning applications. Every business starts with the customers, and CRM is the primary tool that covers the needs of the departments that work with this critical detail.
CHOOSING BETWEEN ERP AND CRM
ERP implementation is a big effort in comparison to CRM. It may require months or even years of analysis of all the business processes, customization, and employee training. Certain types of businesses don’t have inventory, manufacturing, or logistics. Consulting or call center companies are some great examples. Those companies have people as their main asset to function using CRM, accounting, and task management/ tracking applications, such as JIRA. Besides, they don’t need to interconnect the datastreams that tight. Thus, implementing and supporting a vast ERP system will be an overkill for them. Both types of systems have different features and functionalities, and choosing between the two can be difficult for businesses. Here are some of the aspects that you may consider while deciding on ERP vs CRM:
When deciding between an ERP and CRM system, the first step is to determine the specific needs of your business. If your primary concern is managing the various functions of your business, such as accounting and inventory management, then an ERP system may be the best choice. However, a CRM system may be the better choice if your primary concern is managing customer interactions and improving customer engagement and retention.
Another important consideration is scalability. As your business grows, it will require more advanced features and functionalities, so you want to ensure that your chosen system can scale with your business. ERP systems typically have more advanced features than CRM systems, which can be beneficial if your business requires more in-depth management of operations. On the other hand, CRM systems are often simpler and easier to set up and use, which can be beneficial for small businesses.
Additionally, you may want to consider integration. An ERP system can be integrated with a CRM system to create a more comprehensive solution. For example, if you use an ERP system to manage your inventory and financials, you may want to integrate it with a CRM system to track customer interactions and improve customer engagement and retention.
ERP systems tend to be more expensive than CRM systems. However, collaborating with an ERP software development company can be more cost-effective in the long run, as they can automate and streamline many different business functions while providing more advanced features and functionalities. On the other hand, a CRM system can be a more cost-effective solution for smaller businesses that only require basic customer management and sales tracking features.
Another important consideration when choosing between an ERP and CRM system is the level of customization and flexibility. ERP systems often offer a wide range of customization options, which can allow businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs and workflows. This can be especially useful for businesses with unique processes requiring a more specialized solution. On the other hand, CRM systems may have fewer customization options, but they can often be easier to implement and use out of the box.
It’s also worth evaluating each system’s data analytics and reporting capabilities. ERP systems often have more robust analytics and reporting functionalities, which can help businesses to make better-informed decisions and identify areas for improvement. Meanwhile, CRM systems tend to focus more on sales and customer engagement, with less emphasis on data analytics and reporting. However, some CRM systems may still offer some level of data analytics and reporting features.
Another important factor to consider is the level of automation offered by each system. ERP systems often have more advanced automation features, such as automated inventory management and purchase orders, which can help improve business operations’ efficiency. On the other hand, CRM systems tend to focus more on sales, customer engagement, and may not have as many advanced automation features.
In addition to these key factors, it’s essential to consider the user experience and ease of use when choosing between an ERP and CRM system. If your business has a relatively small team, or if your employees are not very tech-savvy, it may be more beneficial to choose a system that is easy to use and navigate. This can minimize the required training and support required, ultimately saving your business time and money.
ERP VS CRM: IMPLEMENTATION AND MAINTENANCE COST
Implementing an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system or customer relationship management (CRM) system can be a significant investment for any business. The cost of implementing an application can vary depending on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of the organization, the specific solution chosen, and the scope of the project.
One of the primary costs associated with implementing the software is the cost of the product itself. The cost can vary widely depending on the vendor, the specific features and functionality offered, and the number of users. Some solutions may be available on a subscription basis, while others may require a one-time purchase or licensing fee. Additionally, some apps may be customized to meet the organization’s specific needs, which can increase the cost of the software.
Another cost to consider is the cost of installation and customization. This can include the cost of configuring the system to meet the specific needs of the organization, as well as the cost of any customization or integration required. This can also include costs for training, testing, and implementing the new software. It’s important to note that chosen applications can require a robust infrastructure to support the implementation, and businesses might have to invest in additional hardware and network.
The cost of ongoing support and maintenance is another important factor to consider. Many ERP and CRM vendors offer support and maintenance packages, including software upgrades, bug fixes, and technical support. The cost of these packages can vary depending on the vendor and the level of support required. Some vendors may also offer additional services such as consulting and training, which can also add to the cost of the system.
In addition to these direct costs, indirect costs are associated with implementing business software. This can include the cost of employee training and the loss of productivity while employees learn to use the new system. Considering these costs and planning accordingly to minimize their impact on the business is important.
What more information on ERP pricing?
Did you know you can build your own ERP system built and tailored to your business needs?
Read a complete guide to a custom ERP solution development cost
While the cost of implementing an ERP system can be significant, there are also many benefits that can justify the investment. ERP systems can help businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase revenue. To help manage the costs of an ERP system, it’s important to research and compare different ERP solutions, choose a vendor that is reputable and offers good support and services, and to have a realistic budget and plan in place. Additionally, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the needs and goals of the organization to choose the ERP solution that best meets those needs and is the most cost effective for the business. By taking these steps, businesses can minimize the costs associated with implementing an ERP system and maximize the benefits that can be gained from the investment.
CONCLUSION
When deciding between an ERP and CRM system, it’s important to determine the specific needs of your business, consider scalability, integration, budget, vendor and support options, customization and flexibility, level of data analytics and reporting, level of automation, user experience. It can also be an option for businesses to use an integrated ERP and CRM system. By considering these factors and evaluating your organization’s unique requirements, you can make an informed decision that will help your business grow and succeed in today’s competitive business environment.
In conclusion, both ERP and CRM systems can be extremely beneficial for businesses, but the choice between them will depend on the specific needs and goals of the organization. While ERP systems can provide a more comprehensive approach to managing the different functions of a business, CRM systems can improve customer engagement and retention, increase revenue and conversion rates, and provide analytics and reporting on customer behavior. It’s important to evaluate your business’s specific requirements and weigh each system’s pros and cons to choose the one that best meets your needs.
Looking for professional assistance in choosing between ERP and CRM systems?
Existek is a software development company that has extensive experience in delivering both ERP and CRM solutions. We can help you create your custom software regarding your business-specific needs.
Frequently asked questions
What is CRM software?
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software is a type of business software that helps companies manage interactions with customers and clients. It can be used to store and organize information on customers, such as contact information, purchase history, and communication logs, and it can also include features for automating tasks like marketing campaigns, sales tracking, and customer support. The goal of CRM software is to help businesses better understand and engage with their customers, ultimately leading to improved sales and customer satisfaction.
What is ERP software?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a type of business management software that helps organizations automate and manage various business processes, such as accounting, human resources, procurement, and customer relationship management. ERP software typically includes modules for managing different aspects of a business and can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization. The goal of ERP software is to provide a single, integrated view of a business's operations, which can help organizations make better decisions, improve efficiency, and increase profitability.
What is the difference between ERP and CRM?
Even though these are both types of business software, they serve different purposes. CRM software is focused on managing relationships with customers, while ERP software is focused on managing and automating internal business processes. CRM can be one of the ERP software modules, but it's not necessary; ERP can work without CRM.
ERP vs CRM: how to choose?
The choice between ERP and CRM software will depend on the specific needs and goals of your organization. It's important to evaluate the features and capabilities of different software options and to consult with experts and vendors to determine the best solution for your organization.