Updated: February 28, 2025
Published: November 4, 2020
EDI is often mentioned in the context of large and small businesses. It is a system that makes document exchange fast, efficient and accurate. Those who don’t employ EDI in their business make people responsible for data entry and transmission. It may lead to numerous mistakes, and therefore, spoiled customer relationship. Read the article to find out what is EDI, and how to make your business benefit from using it.
List of the Content
- EDI definition: what is EDI
- EDI documents
- What is EDI software and how typical EDI workflow looks like
- Benefits of EDI
- EDI implementation
- Challenges of EDI
- In conclusion
EDI is often mentioned in regard to many business domains. So what is EDI and why is it mentioned so frequently in discussions about workflows of both SMEs and enterprises? At a glance, the answer is pretty simple. EDI stands for Electronic Data Interchange. It is the set standards that are applied for internal and external electronic data interchange between various business divisions, government structures, and companies. However, this standard has been applied since the late 1980s thus a simple definition can’t represent all the depth behind it.
Various definitions of it may seriously confuse those who are trying to understand its concept, how it works, why, when, and what’s more important, how to use it. In this article, we’ll try to give you the clearest possible answer to “What is EDI?” and “How is it leveraged in various mediums?”
EDI’s generalized definition is not sufficient to realize its main idea so we’ll also look at how EDI works exactly, what are the reasons to implement it, and what it is necessary to know to start using EDI in your business scheme.
EDI DEFINITION: WHAT IS EDI
Let’s start by giving more detailed answers to the questions “What is EDI”, and “What does EDI stand for. Electronic Data Interchange is a set of means allowing business process participants to exchange some commercial documents without almost any human intervention. In this context, “means” imply specialized software and particular standards that define many commercial aspects, such as industry type, RFQs, POs, invoices, etc. (these terms will be considered in the next paragraph). EDI is a kind of document flow between two computers that are performed without human help. Humans’ role in this process is to handle errors, check the quality of the performed transmission, and fill some documents themselves only in special situations. In order for a computer to perceive the data properly, the document has to be formatted strictly. For this, there exist various standards that define properties of each document type, how it must be filled, typical fields, data structure, etc. These guidelines vary for different industries. For example, trading, transportation, and medical companies will fill electronic documents differently. The main point of EDI is to establish an automated exchange of commercial messages with the lowest error rate possible. In real life, failures happen because of human mistakes, thus, EDI is purposed to lessen the human’s part in transmissions and utmost automate it.
What is EDI in simple words?
In common words, EDI can be described as a document flow between business partners’ computer systems. This exchange is done without human participation. All documents are formed by the machine itself, interpreted and transmitted by it as well.
The first time, the American military transportation company implemented EDI in the 1960s in order to achieve high accuracy in document delivery. Why EDI had to be employed is the fact that the amount of data that had to be transmitted exceeded the usual norms, and doing it manually would take a lot of time and other resources. Needless to say, it also led to multiple mistakes and failures. Among world-known giants, one of the first to implement EDI in the 1970s was Heathrow Airport. Later on, there was created the DTI (direct trader input) method. It implies that the information is inputted by the DTI user who is responsible for all the transmitted data. DTI allows making the clearance part lightning-fast and then delivering the info right into the customs computer system. Huge businesses, having acknowledged the benefits of DTI, made it integral to EDI in the 1980s. After the existing benefits of EDI were totally recognized, there appeared a need to somehow systematize performed processes. That’s when such protocols as X12, EDIFACT, ODETTE, and others were created. They were designed for different industries and regions. That’s how EDI got started. Nowadays, EDI is a technology used by a great number of commercial and governmental organizations who want to boost their productivity and quality of the services delivered.
EDI Glossary: EDI Terms To Know
You already know what is EDI itself but, as this article will be filled with specific expressions, let’s draw up a small glossary of the EDI terms to understand the concepts better.
RFQ (request for quotation) is a commercial offer. This document implies specifications, services offered, prices, quantities, etc.
PO (purchase order) is the next stage after forming RFQs. It is a kind of confirmation to it. The document implies mostly the same information as the RFQ.
Invoice is the same thing as PO but sent to a purchaser, unlike the PO that is sent to the vendor.
The DTI concept is already explained. It is a method allowing sending data right to the recipient’s system.
X12 is the most used EDI standard in the US and North America.
EDIFACT is a versatile standard that allows exchanging information between different countries who have ratified this standard.
ODETTE is a protocol for transmitting data between European countries.
VAN is an intermediary network between the traders that keeps, processes, and sends the data. These networks are owned by third-party companies that are specializing in EDI services. VAN providers are serving as intermediates between agents in Electronic Data Interchange networks and add an extra level of convenience for senders and receivers for a fee.
AS1-AS4 (Applicability statements 1-4) are specifications that allow businesses to exchange secure emails over the HTTPS protocol. The first version used SMTP but the next ones were modified, thus, achieving higher security.
FTP stands for file transfer protocol. It is one of the first methods to exchange data. It uses the Internet and allows to transfer messages independently of the OS.
How Does EDI Work
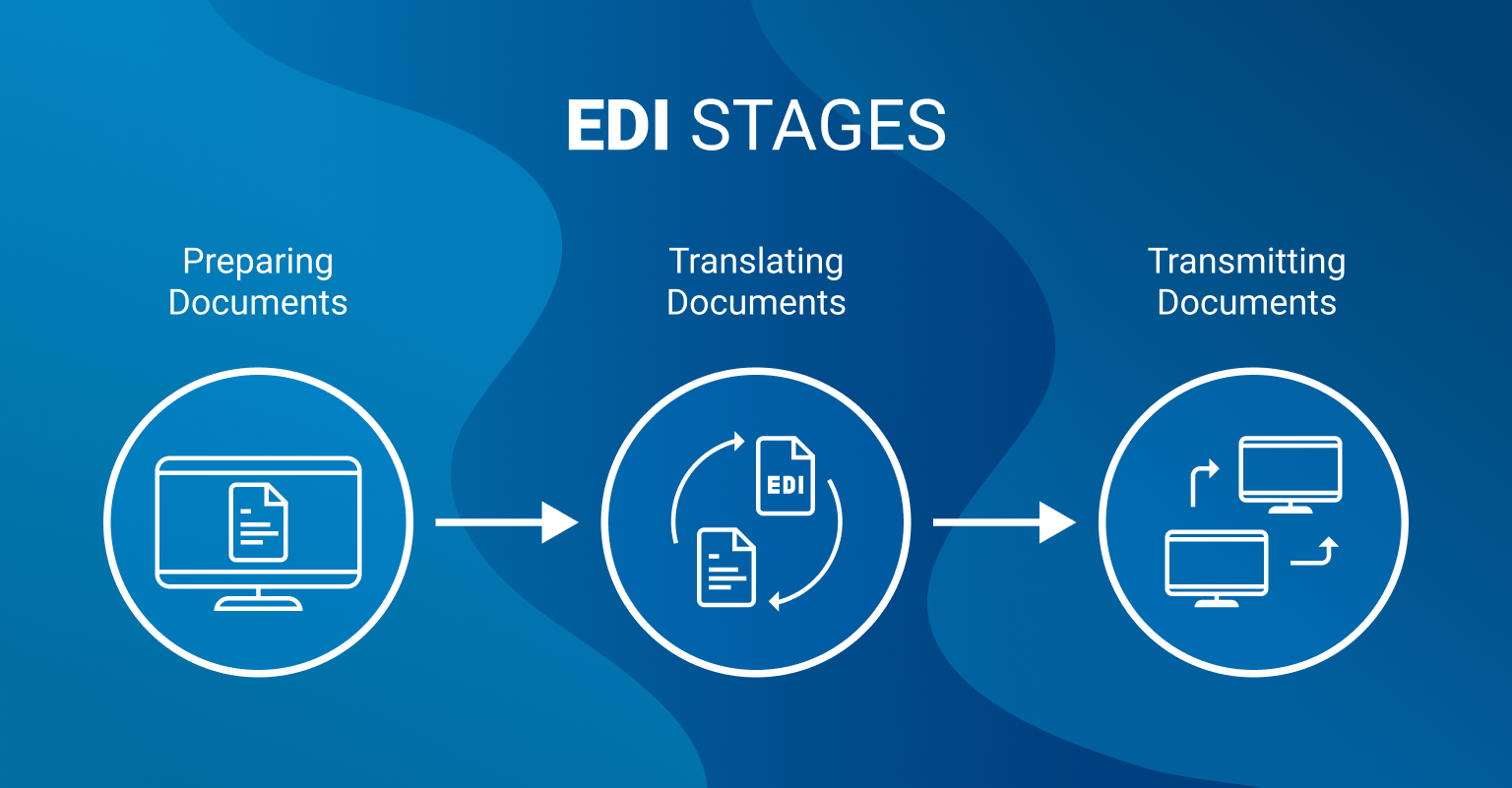
EDI is a very complex notion and answering the question “How does EDI work?” might be tricky. However, we’ll try to explain this process as clearly as possible. The overall process can be divided into three stages:
- Preparing EDI documents. At this point, the sender has to prepare the document with an order. The data has to be organized in such a way that it will be read by the EDI software, thus, instead of printing a PO (purchase order), the system creates an electronic version of it and optimizes it according to EDI standards. Among the approaches for document preparation, there are importing data instead of reprinting it manually, reformatting electronic docs into the data files, and purchasing ready-made EDI software.
- Translating them into the EDI format. This step requires leveraging specialized EDI translation software. Such apps divide the data into proper segments and elements. To get past the purchasing of the software, you can send the data to the EDI service provider, and he’ll do this task. By the way, the provider enables interpreting documents not only to but also from the EDI format.
- Transmitting documents. To transfer EDI documents, traders use three main approaches:
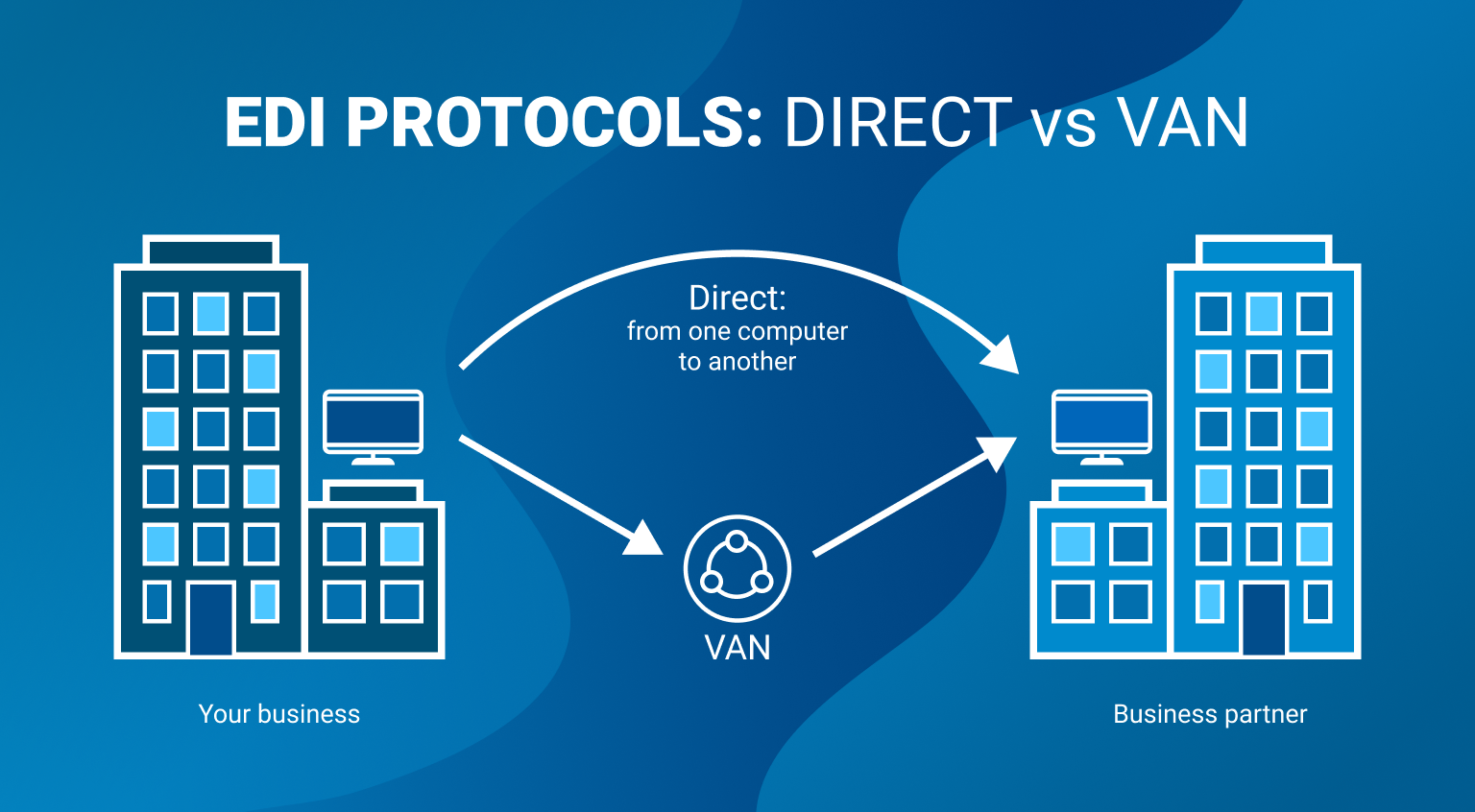
- Direct. It is performed via an exact secure Internet protocol directly from one computer to the other
- Via the VAN. The data is sent to the service provider, and from there, it goes to the recipient
- Mixed type. Used while transmitting large amounts of data is essential. A part of it may be transferred directly, and a part via the provider.
Using VAN to deliver documents may be rather expensive as the fee is taken by the VAN networks owning companies for each transmission. However, it may help you save some setup costs.
Documents are encrypted, and apart from this, passwords and identifications are used to achieve higher security during the document exchange. Ways of protecting information depend on the protocol you’re using, so while integrating the EDI, choosing the right protocol for your business is necessary.
One more thing to mention is that while establishing your business, it is important to become EDI capable. This term means that you’re using the software proper for EDI implementation and that it allows applying both client and vendor-side encryptions, etc.
Types Of EDI Protocols
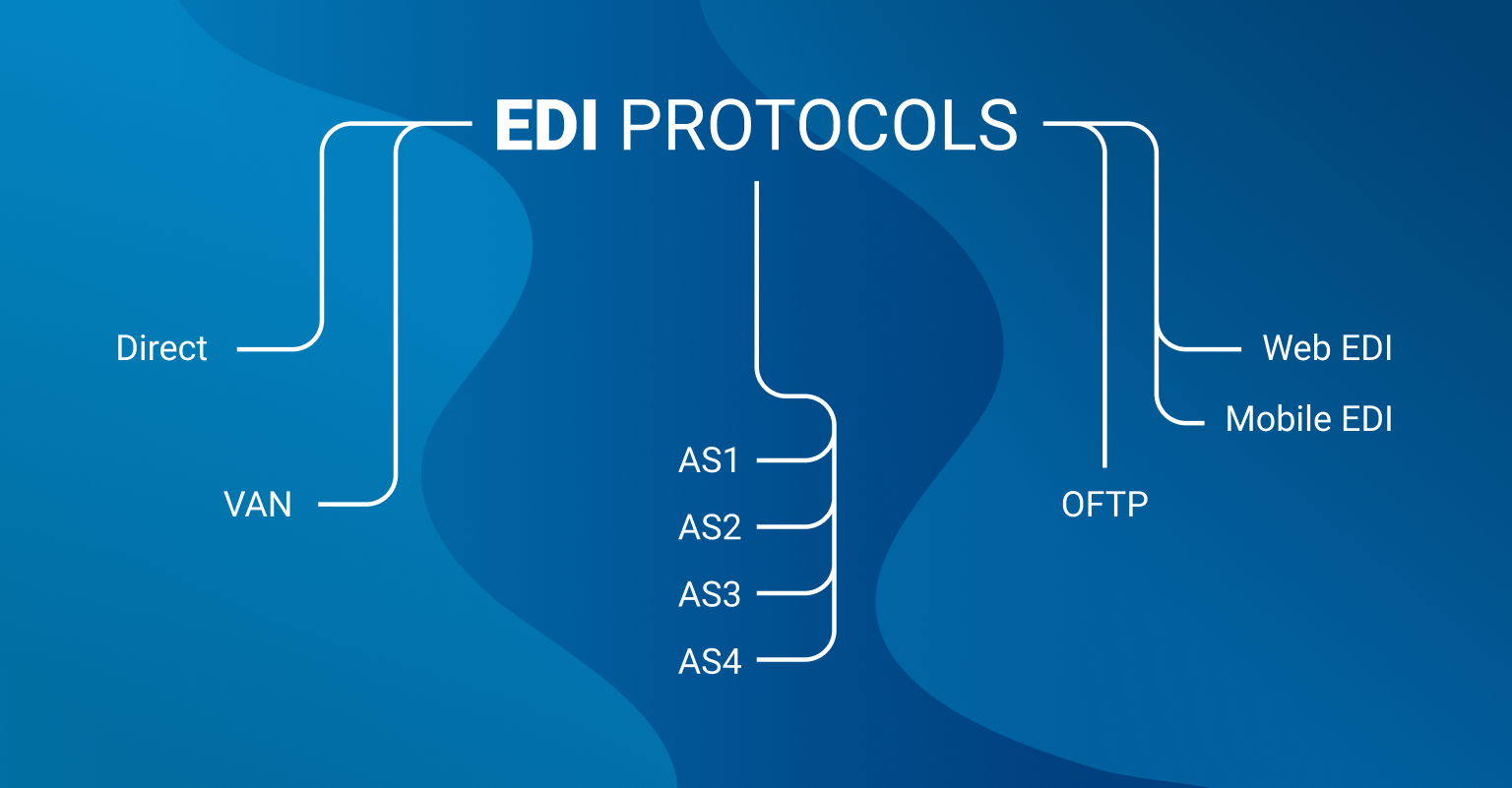
There are many types of EDI protocols. They contain some guidelines that differ according to the business type, region, and other factors. Choosing the proper one depends on what is EDI going to be used for. Among the most often-used protocols there are:
- Direct and VAN (described previously)
- AS1 sends the data with the help of email protocols. Files are sent in the form of attachments. This version of AS protocol is not secure enough as it allows optional encryption of the messages.
- AS2. Most often used protocol due to its simplicity and security. Sends information over the HTTPS, which means the most secure end-to-end encryption.
- AS3 isn’t designed to replace the AS2 but has certain benefits to those kinds of users who imply FTP in their business as it is built on its basis thus the basics are the same. However, it is much more secure than FTP and has higher application interoperability. For the great majority of traders, AS3 is not secure enough
- AS4 was made as an updated version of AS2. It has almost the same features but is easier to set up and maintain further on
- OFTP is a technology created exactly for B2B docs. Initially, it was built for point-to-point communication but now it is optimized the way it can easily work with VAN
- Web EDI is probably the simplest form of EDI communication. It is performed with the help of online-shared forms. Documents there can be created, updated, and changed. Such an option is suitable for small and mid-size businesses as web EDIs are still not optimized for the large data transfer
- Mobile EDI replicates the idea of the previous type but on mobile devices. The process starts with scanning the barcodes, and then as in the other cases: reading info, interpreting it, checking, setting, etc. More and more businesses want to imply mobile devices in their supply chain so mobile EDIs are becoming very popular
EDI DOCUMENTS
Let’s begin with what is an EDI file. It is a document with some data saved strictly formatted according to one of the EDI standards. The data in them is kept only in the text format. EDI document is used to directly transfer commercial information. There are a lot of EDI document types but the most common include:
- XML types (cXML, ebXML, etc.)
- xCBL
- ANSI
- X12
- CSV
- EDIFICE
- EDITRANS
- ETIS
EDI document types are used for different industries, e.g., the last three are designed for information technology, transportation, and telecommunication companies accordingly.
WHAT IS EDI SOFTWARE AND HOW TYPICAL EDI WORKFLOW LOOKS LIKE
If you’re dealing with some major businesses, you have to be ready to implement EDI software as nowadays, big companies want to employ it In the working process to save time, costs, and other resources. Let’s start with what is EDI software. It is a set of tools that help to perform all the necessary operations. They include formatting documents into a proper file type, integration with BDs and backend processes, and transmitting messages among the traders.
The first thing EDI software does is interpreting data to the EDI format and the next step this phase includes is mapping. It is a reverted process. When a recipient gets an EDI file, he uses mapping in order to convert an EDI doc into a flat format that can be opened with an ERP program, for example.
Document transmission is the next step. The software enables the opportunity to send files via multiple protocols without using VANs. It used to be challenging not so long ago but EDI software provides point-to-point communication via one of the secure protocols listed previously in the article.
Integrating EDI with your backend technologies is the most expensive yet important stage. Modern EDI software uses API-first structure and ports to connect to your ERP application, or CRM system, read data from there and form the needed documents in the EDI format on its basis.
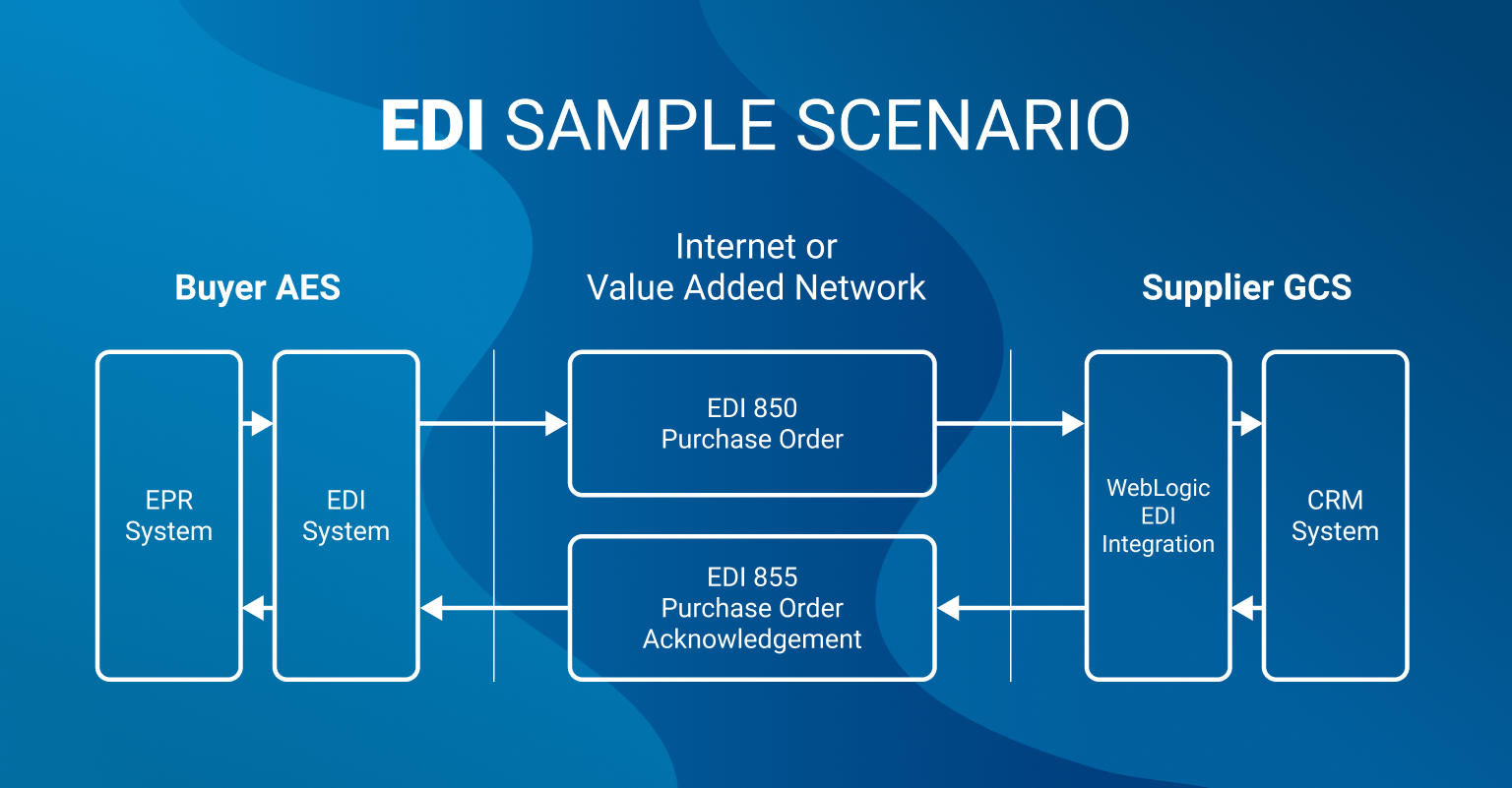
Let’s see how the typical EDI document workflow looks like:
EDI Document Sample With Explanation
EDI documents may be of different formats. The 5 most common types are:
- UN/EDIFACT
- TRADACOMS
- UBL
- ANSI ASC X12
- VDA
Each of these types has certain guidelines and markups. Each type is like a particular language that can be written and read by the sender and recipient’s machine accordingly. The main goal of each format is to make sure that all data elements are in the proper places and in the proper sequence so the computer can understand what each symbol means. As in any language, such guidelines form syntax. Codes are used as identifiers for countries, currencies, etc.
Altogether, the crucial point of the EDI process is to make certain that both supplier and recipient’ machines are using the same markup defined by the EDI format.
Every EDI format includes these three big components:
- Elements
- Segments
- Transaction sets
Comparing an EDI format to a language, elements would be letters, segments – words, and transaction sets – sentences.
We’ll look at the EDI document example using probably the most used format – UN/EDIFACT. It has such a set of segments: PICTURE. For a better understanding, look at the example of the EDIFACT order (groups of symbols in bold are EDIFACT segments):
EDI Software Types
Web VAN EDI is the first type. It doesn’t employ any application, it is performed via the Internet. In this case, you send the data to the VAN server, and they translate it all into the EDI format, and then send it to your business partner. They also do the mapping when you are a recipient. The costs are spent on both connecting to the VAN network and switching it for another, exceeding a certain size of the file, and each document transaction. This option is not good enough for large businesses because VAN networks cannot connect to your databases so you’ll have to input the information yourself, which leads to mistakes and great time waste.
Single-purpose solutions come next. They are relatively cost-effective, and also reduce the number of possible errors but, as it is clear, they are designed to manage only one task at a time, whether it is translation, transmission, or backend integration.
End-to-end solutions, unlike the previous type, handle all three tasks but they are more expensive and their setup might be quite challenging.
Integration-specific apps are designed to work only with the backend. They guarantee that the data is read and saved without any mistakes. Such solutions integrate well with different applications and databases, even those that are not designed to work with EDI.
Industry-oriented software is the last option. Platforms for a certain field are quite popular among the manufacturers as they have flexible API allowing them to perform the human part of work fast and correctly.
What is DMS and how much does it cost?
You can either buy EDI software or build your own DMS system that supports required EDI formats.
While having decided on working with EDI, you have to choose a deployment option. They are not different from those for other kinds of software: on-premise, hybrid, cloud, PaaS (infrastructure/platform as a service). Needless to deepen into these concepts. It’s enough to say that you’ll get all those pros and cons from each option as in the case with any application. On-premise is more difficult to set up and maintain but provides higher security. Cloud and iPaaS are fast and easy to employ but depend on the Internet connection. Hybrid has almost no disadvantages as it works with different platforms, available online, and secure enough.
What deployment options do I have while working with EDI?
The deployment options of EDI are quite usual: on-premise, hybrid, cloud, and iPaaS (infrastructure/platform as a service). Which one to choose is up to you. However, consider that cloud and iPaaS are faster than on-premise but hybrid solutions have bypassed them all (it is highly secure, cross-platform, and fast).
BENEFITS OF EDI
After we’ve understood what is EDI and figured out how does EDI work, let’s see what are the practical advantages of using EDI, and why it is a good idea to implement EDI solutions in your business. The main upsides are:
- Fast processing. Document transactions take minutes instead of days spent on sending postal mail, or hours for writing electronic letters, and filling them with information manually. In addition, the work based this way requires fewer people thus, the staff that might have been busy with manual work can now do more valuable jobs. Real-time tracking, as a function of any EDI software, ensures both coworking sides that messages are delivered in time.
- No human errors. While gathering business information, filling it in the documents manually, sending them by email, tracking letters, etc. there is a great chance that there will appear mistakes at some point, be it the loss of messages, problems with secure delivery, or simple inattention.
- High accuracy is a solution to the problem described in the previous point. Because each process in EDI is automated, the data is gathered, interpreted, and sent correctly, and always on time.
- Commercial benefit. Needless to say that expenses on paper, printing, storage, and retrieval of documents, filling them, transportations, etc. are drastically reduced by using EDI. It also saves costs usually spent on handling errors, such as lost letters, or rewriting illegible for some reason mails.
- Improved relationships with customers. EDI severely reduces the time gap between ordering a product and receiving it, which leads to more stable working relations between sellers and buyers. Other than that, the absence of errors enhances the level of satisfaction as well.
- Environmental aspects. In the modern world, saving ecology is extremely important, and EDI has its upsides in this area. It allows reducing paper resources by replacing paper letters with electronic faxes, and the level of CO2, usually appearing by using petrol-powered transport.
As you can see, the benefits of EDI are quite versatile. They help to improve the overall efficiency and save such important resources as time, costs, and energy.
EDI IMPLEMENTATION
An EDI implementation is a crucial step for any business, as it ensures that the organization is able to exchange electronic data with its trading partners seamlessly. EDI is a standard format for the electronic communication of business documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. It eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces errors and costs associated with paper-based transactions. The process of EDI implementation involves several stages, including the installation of EDI infrastructure, the establishment of a technical connection with business partners, and the certification of the EDI system to industry standards.
- The first stage of EDI implementation involves installing the necessary software and hardware to handle mapping, translation, transmission, and integration with databases. This includes purchasing and setting up EDI software, such as EDI translators, EDI gateways, and EDI mapping tools. This software will be responsible for converting your internal data format into the EDI format that is understood by your trading partners. Additionally, it is important to establish a secure working space, such as a dedicated EDI server or cloud-based EDI system, to ensure the security and reliability of the EDI transactions. Connecting to VANs is also a crucial aspect of this stage, as it allows for the reliable and secure transfer of EDI data between trading partners. It is also important to ensure that the necessary hardware is in place, such as servers, storage, and network equipment, to support the EDI system.
- The second stage of EDI implementation is the establishment of a technical connection with business partners. This step is essential to ensure that the EDI system is able to communicate effectively with the systems of trading partners. This includes choosing the appropriate EDI standards, protocols, and guidelines to ensure clarity and interpretation of data. For example, EDI standards such as EDIFACT, X12, and TRADACOMS are widely used in different industries and regions. It is important to ensure that the EDI system is configured to use the same standards as your trading partners; otherwise, the EDI transactions will fail. Additionally, it is also important to establish a technical connection with business partners, such as configuring firewalls, VPNs, or AS2 connections, to ensure secure and reliable data transfer.
- The final stage of EDI implementation is the certification of the system to industry standards. Standards are the foundation of the entire EDI ecosystem, and it is essential to ensure that the EDI system adheres to them. This includes tracking standard updates and making any necessary adjustments to the system to keep it in compliance. For example, EDI standards such as EDIFACT and X12 are updated regularly to reflect changes in business practices and technology. It is important to ensure that the EDI system is capable of handling these updates and that the trading partners are also compliant with the updated standards.
Overall, the process of EDI implementation may seem daunting, but by following these three steps, any business can successfully implement an EDI system that is ready to interact with the systems of its trading partners. It is important to complete EDI implementation at the beginning of your business as your trading partners will further require the working EDI space. The process requires careful planning, testing, and coordination to avoid any interruption of business operations. Moreover, it is also important to have a dedicated team or a specialized EDI service provider to manage the EDI implementation, maintenance, and support.
CHALLENGES OF EDI
While EDI has many benefits, there are also some challenges that businesses may face when implementing it. Technical challenges, such as data integration and security concerns, can be complex and costly to address. Let’s consider some of these challenges.
- Technical challenges: One of the biggest challenges businesses face when implementing EDI is the technical complexity of the process. Businesses need to invest in software, hardware, and communication protocols that are compatible with the EDI standards used by their partners. It can be difficult and time-consuming, especially for businesses with legacy or multiple systems. Additionally, businesses need to ensure their EDI systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations.
- Cost: Implementing EDI can be costly, especially for small and mid-sized businesses. Businesses need to invest in software, hardware, and communication protocols, as well as staff training and ongoing maintenance and support. Additionally, businesses may need to pay for EDI services from a third-party provider, which can add to the cost. That can make it difficult for small and mid-sized businesses to justify the expense of EDI implementation.
- Data integration: Integrating EDI data with existing systems can be a challenge, especially for businesses that have legacy systems or use multiple systems. Data mapping and testing are necessary to ensure that the EDI data is accurate and can be understood by the recipient’s system. It can be time-consuming and complex, and businesses need the resources and expertise to manage it.
- Security concerns: EDI data contains sensitive information that needs to be protected. Businesses need to ensure that their EDI systems are secure and comply with industry regulations. This can be a challenge as cyber threats are constantly evolving and businesses need to stay up-to-date with the latest security measures. Ensuring the security of EDI data can also be difficult for small and mid-sized businesses that may not have the same level of resources and expertise as larger businesses.
- Limited adoption among small businesses: Small and mid-sized businesses may find it difficult to justify the cost of EDI implementation, especially if they do not have a significant number of trading partners that use EDI. Additionally, small businesses may find it difficult to adopt EDI due to the lack of technical expertise and resources. As a result, they may miss out on the benefits of EDI, such as increased efficiency and improved supplier and customer relationships.
- Staff training and support: Implementing EDI requires staff training to ensure that employees understand the process and can use the system effectively. Ongoing support is also necessary to ensure the system is running smoothly and address any issues that arise. This can be a challenge for small and mid-sized businesses that may not have the resources to provide staff training and support.
- Data quality: EDI implementation requires businesses to maintain high-quality data. This includes accurate data entry, data validation, and data cleansing. Poor data quality can lead to errors and inaccuracies in the EDI data, which can negatively impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the EDI process.
These are some of the main challenges businesses may face when implementing EDI. It is important for businesses to consider these challenges and develop a comprehensive plan to address them before implementing EDI. This can help ensure that the implementation is successful and that the benefits of EDI are fully realized.
IN CONCLUSION
In this article, we answered the most popular questions about electronic document interchange including “What is EDI”, “What are the benefits of EDI”, and others. Electronic document interchange is undoubtedly a complicated system but we hope that this article helped you figure out its concept.
Want to develop your own EDI software?
Contact EXISTEK, an offshore outsourcing company of qualified specialists. We have the proper skills to build DMS systems with EDI formats’ support. If you have any questions, contact us.
Frequently asked questions
What is meant by EDI?
EDI stands for Electronic Data Interchange. It is a complicated system consisting of rules and guidelines that allow businesses to exchange commercial documents almost automatically, without human intervention. Purchase orders, invoices, etc., are translated into the EDI format - a format that can be written by a machine.
Where is EDI used?
EDI is getting more and more popular in all business spheres. Not all companies already employ it as it requires specific facilities and knowledge, but their number is rising day by day. Originally, it was designed for transportation and retail businesses but today, many other industries use it. Among them, there are manufacturing, utility, healthcare, and others.
What are the advantages of EDI?
Among the main benefits of EDI, there are:
Fast processing. Data exchange takes minutes instead of hours in the case of sending postal mail.
High accuracy. As the documents are no longer filled manually, we can neglect the chance of human mistake.
Commercial benefit. Companies save resources on everything necessary for filling in paper documents.
Environmental aspects including less paper use and less CO2 emission.